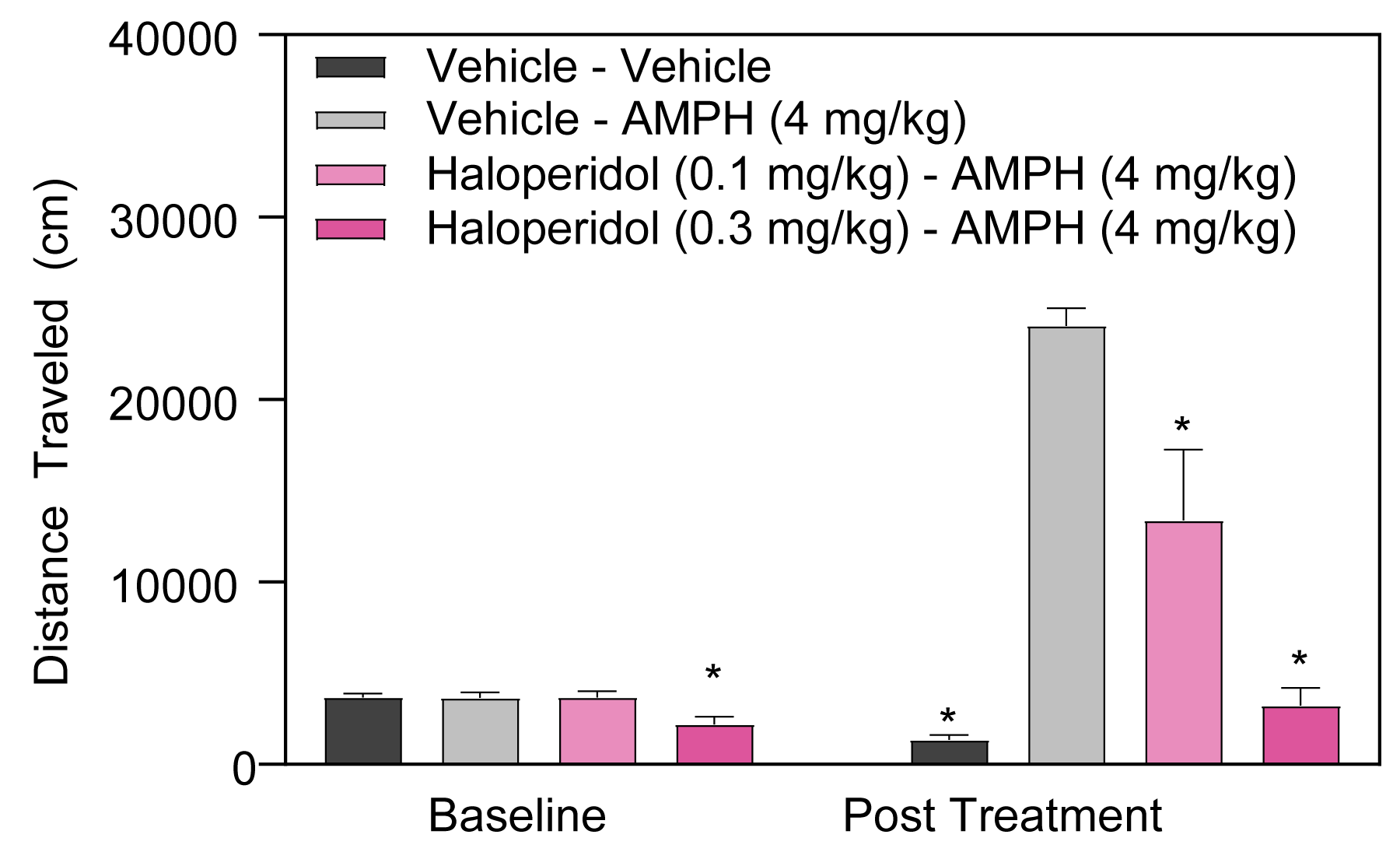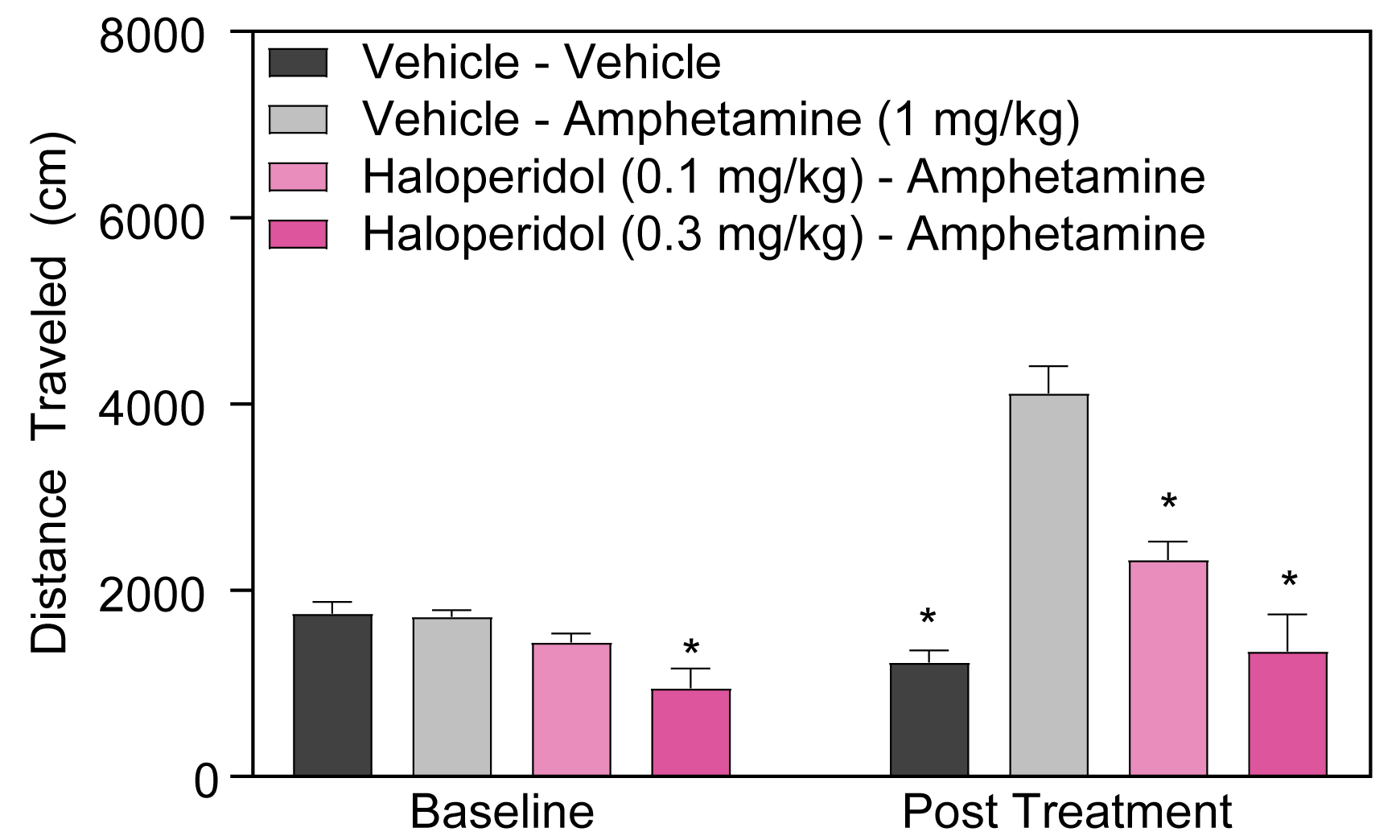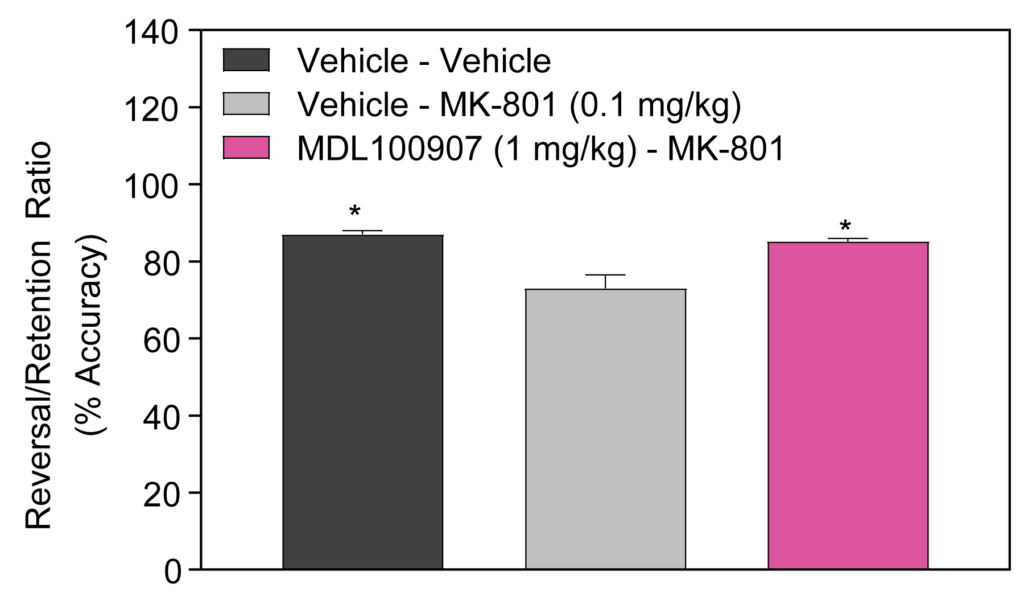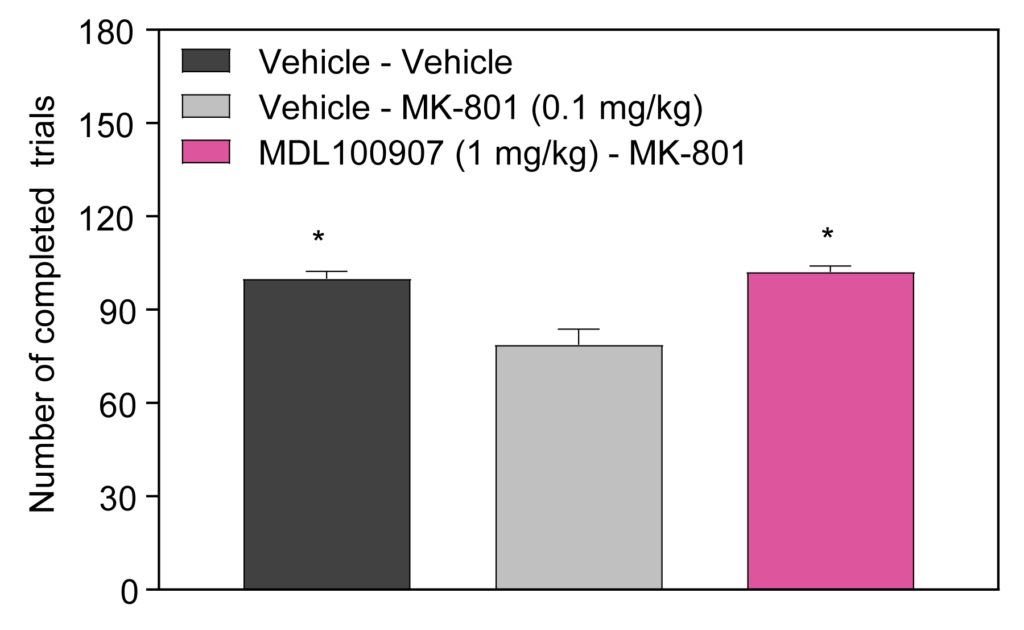Well-Characterized Rodent Models of Schizophrenia
We offer various models that provide valuable insights into the cognitive impairments and other positive and negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia and the impact of your therapy.
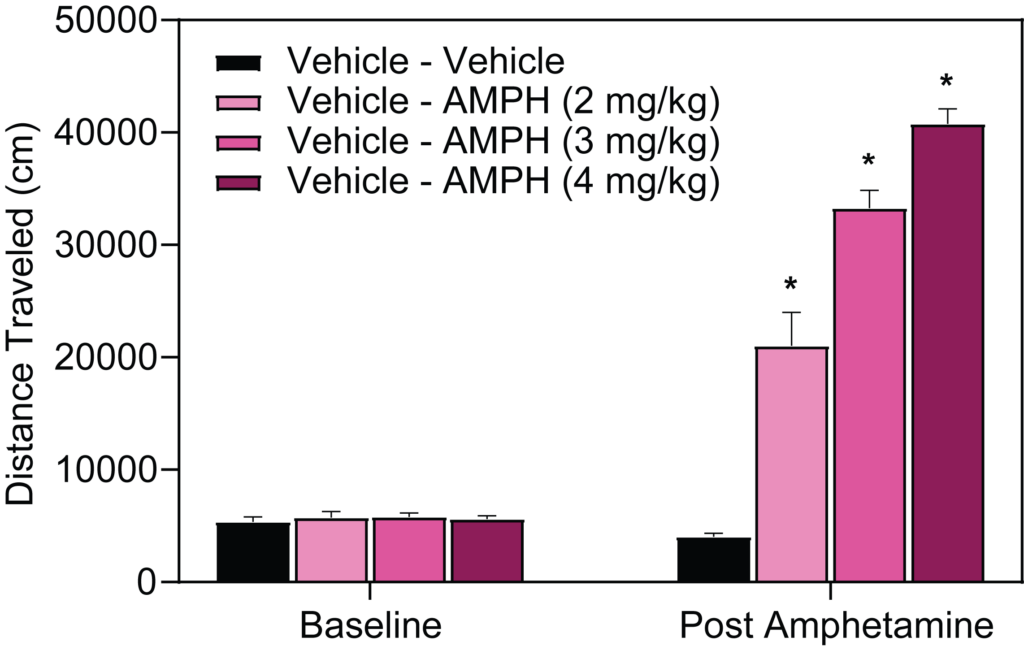
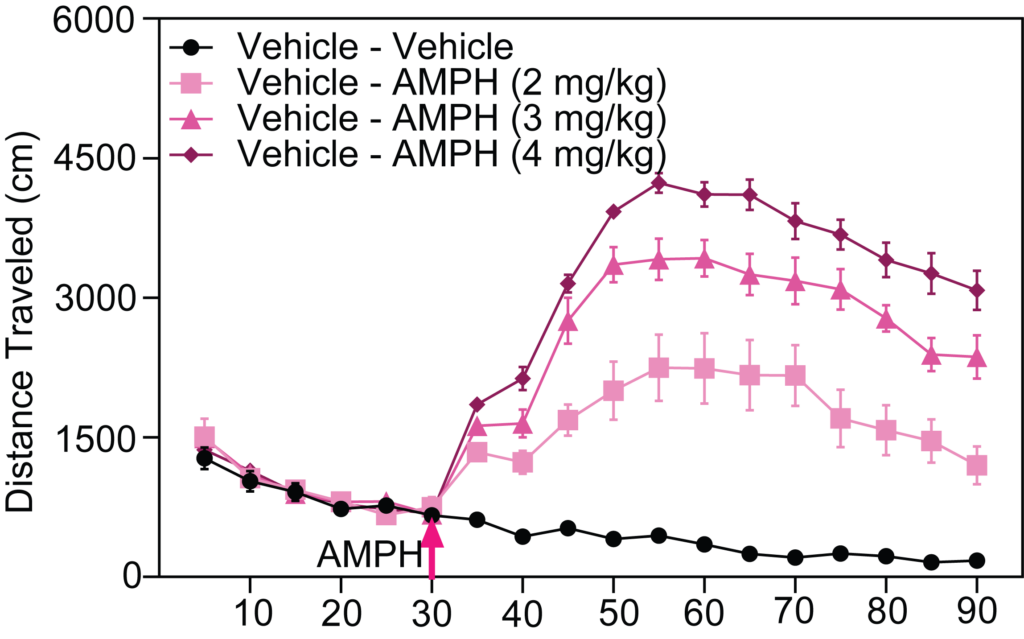
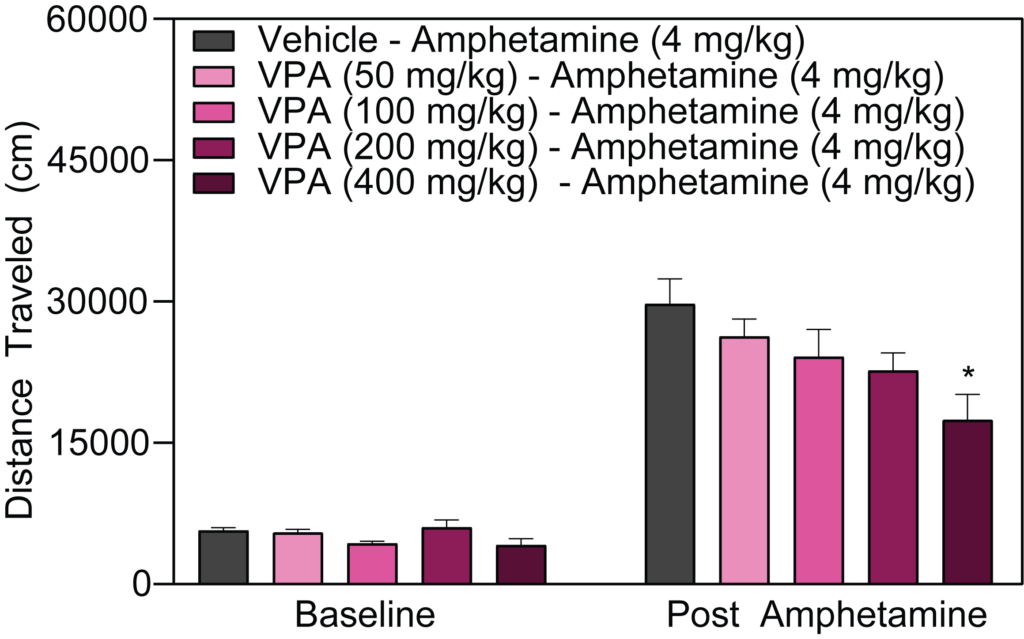
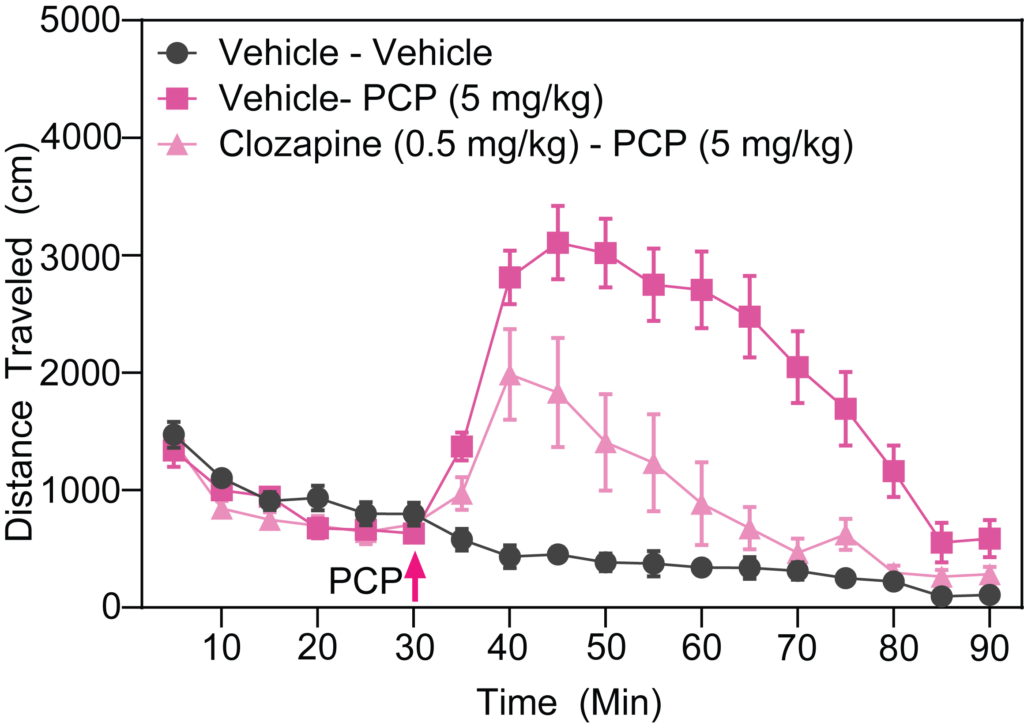
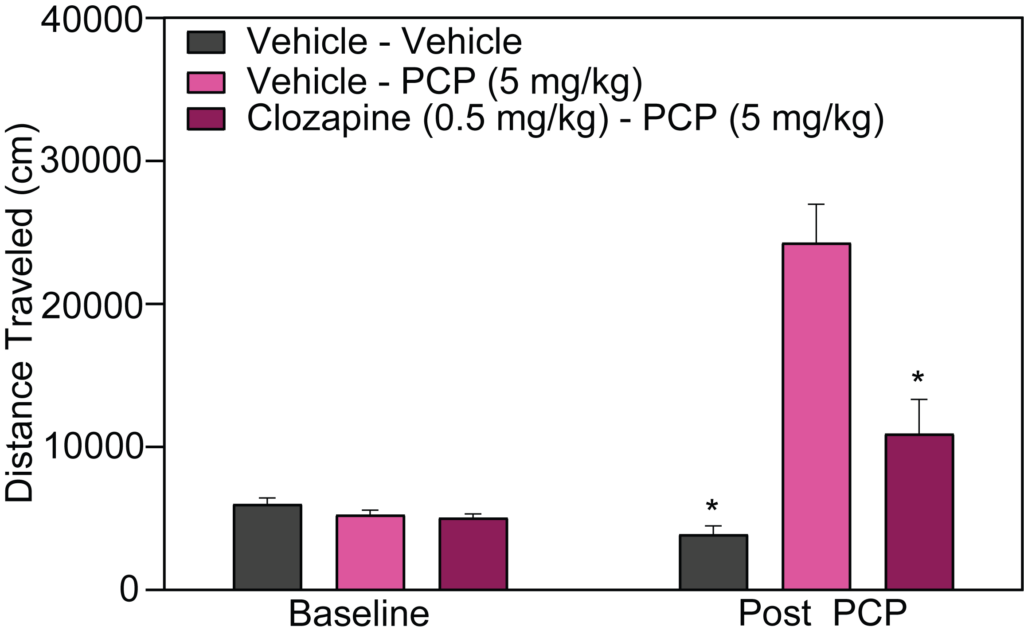
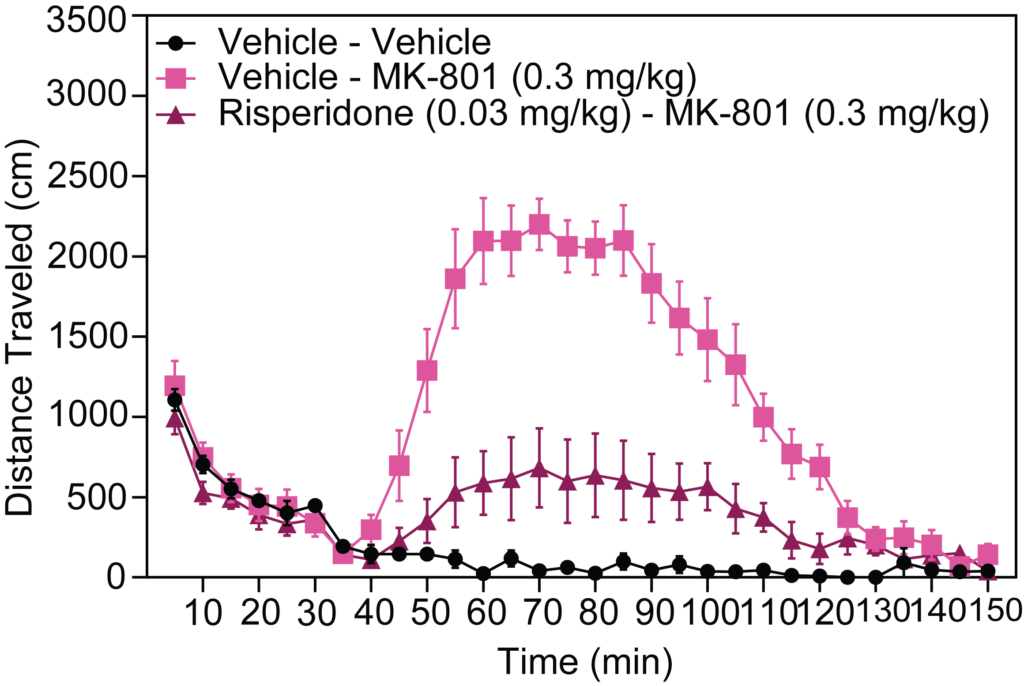
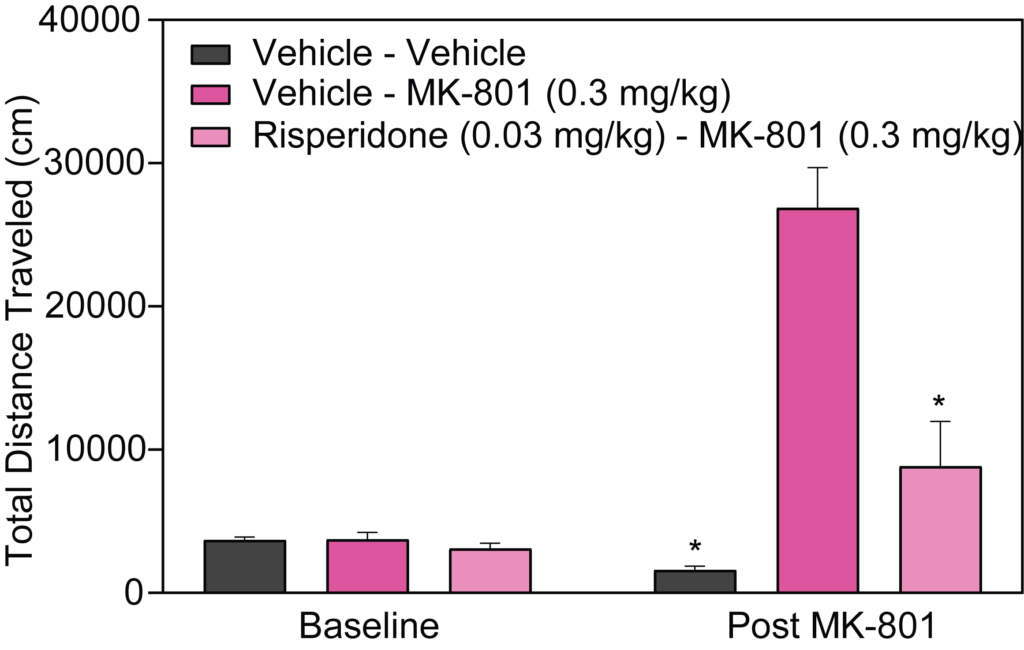
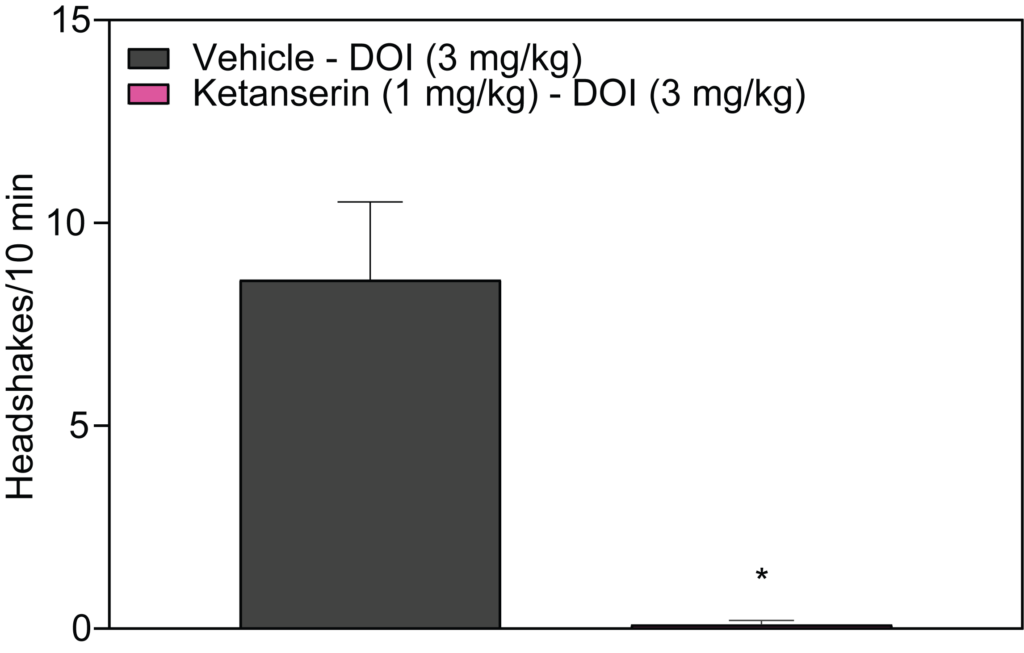
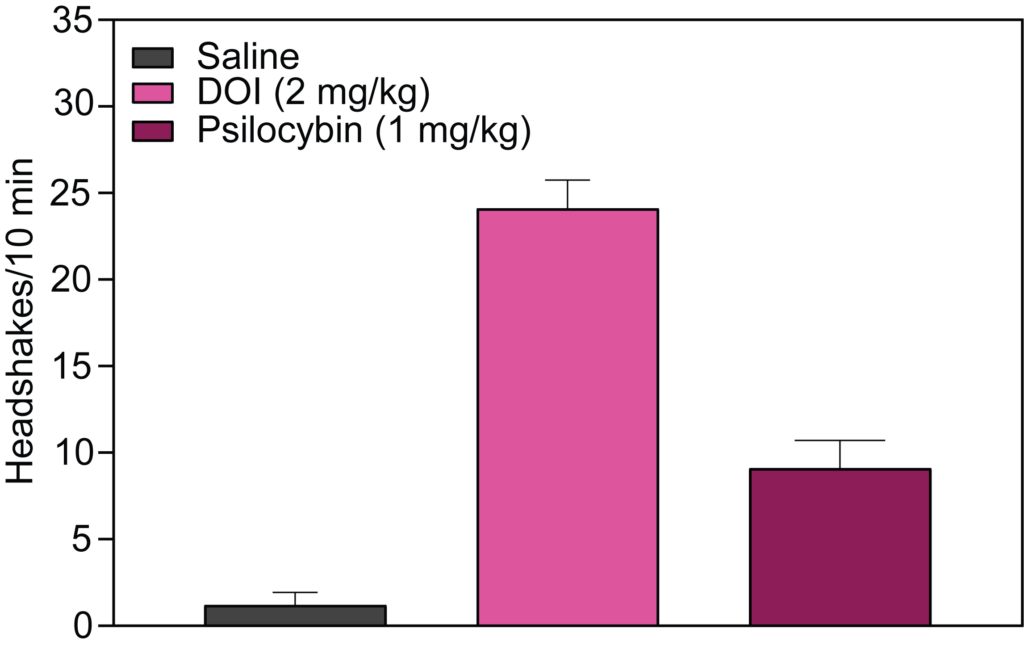
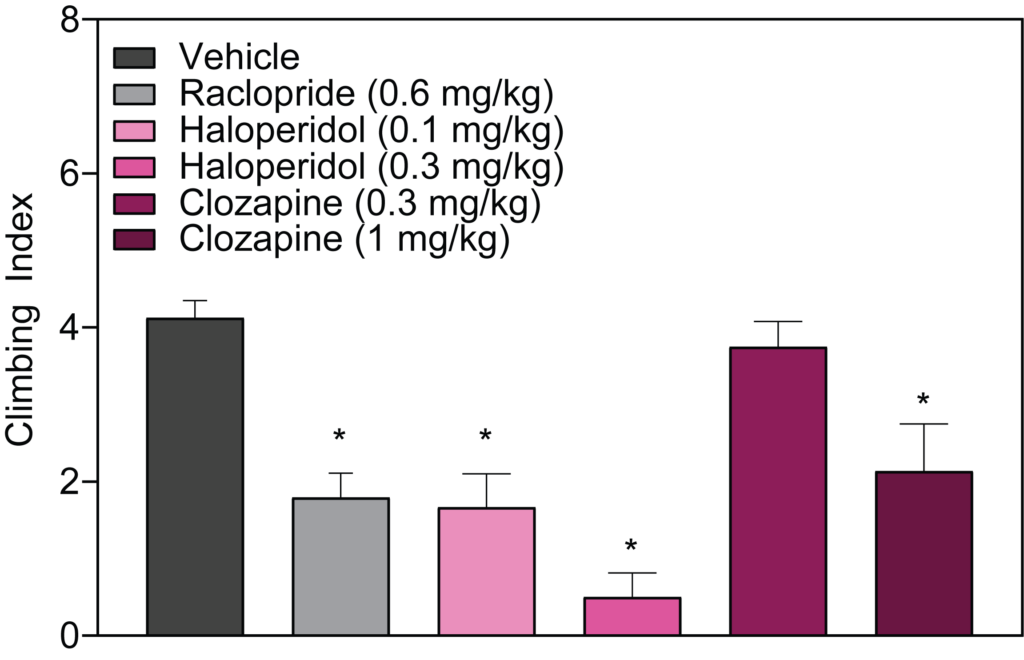
- Stimulant-induced activity (locomotion, headshakes, rearing and climbing)
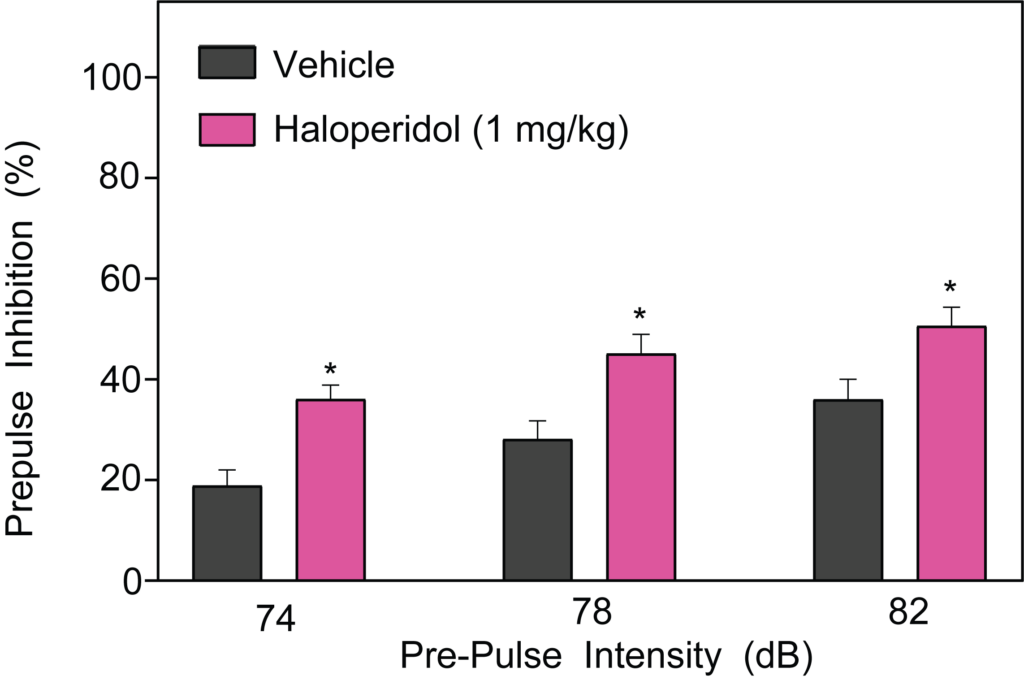
- Pre-pulse Inhibition of Acoustic Startle
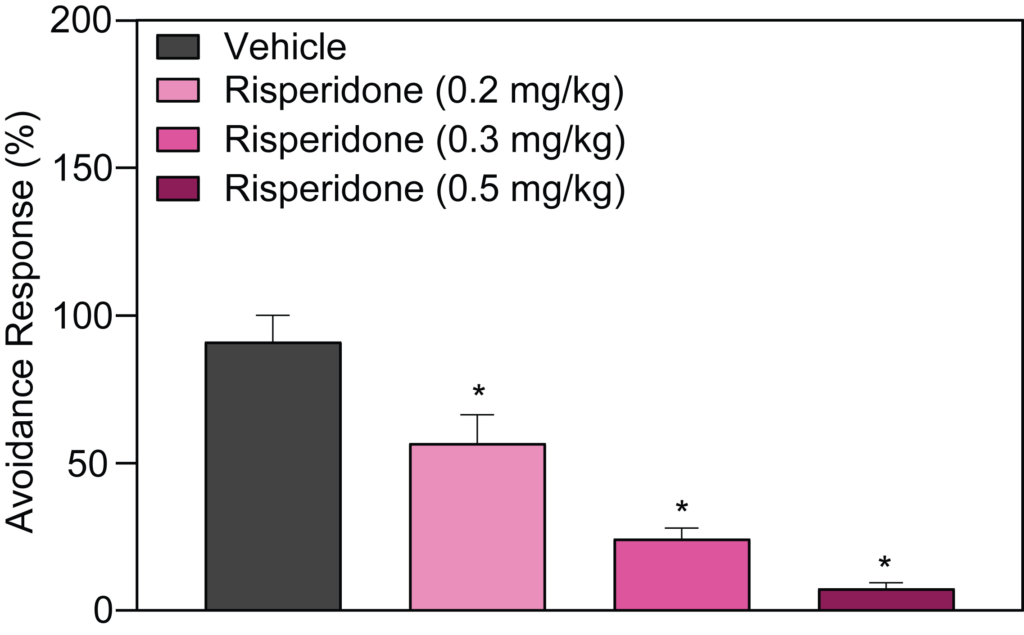
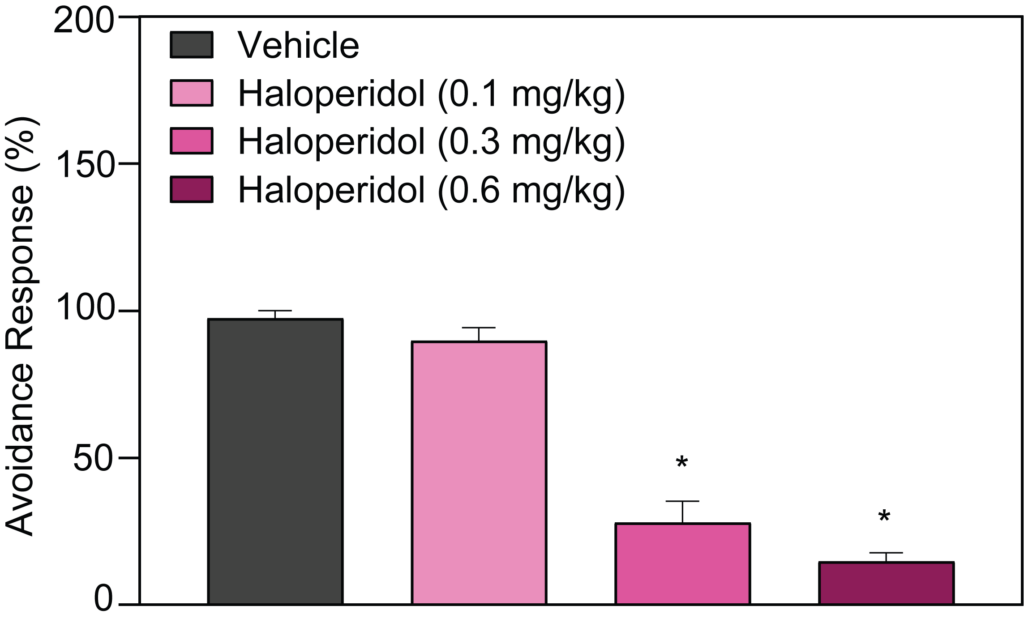
- Conditioned Avoidance Response
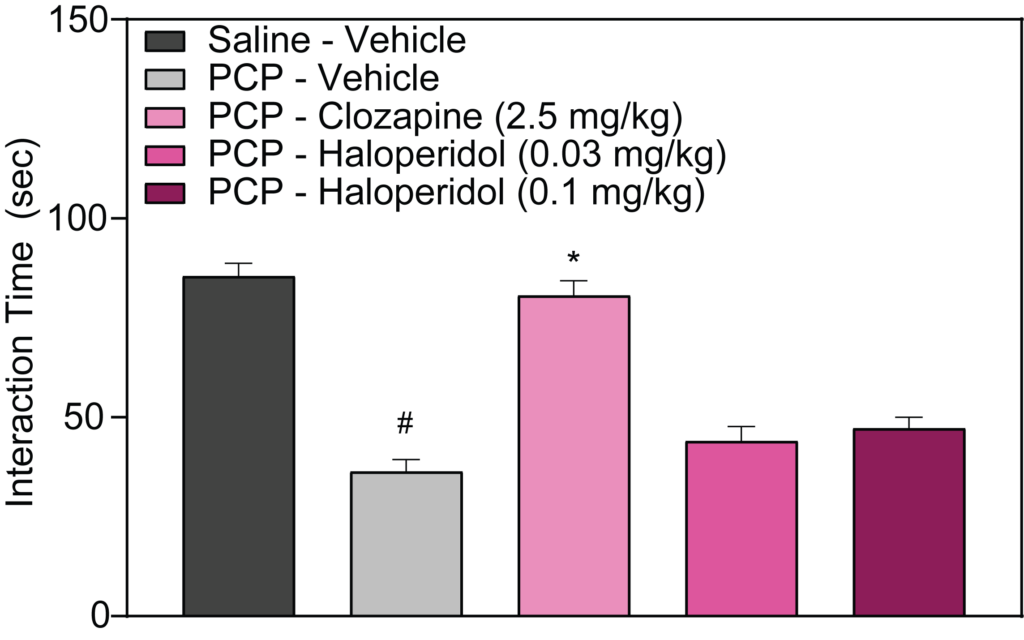
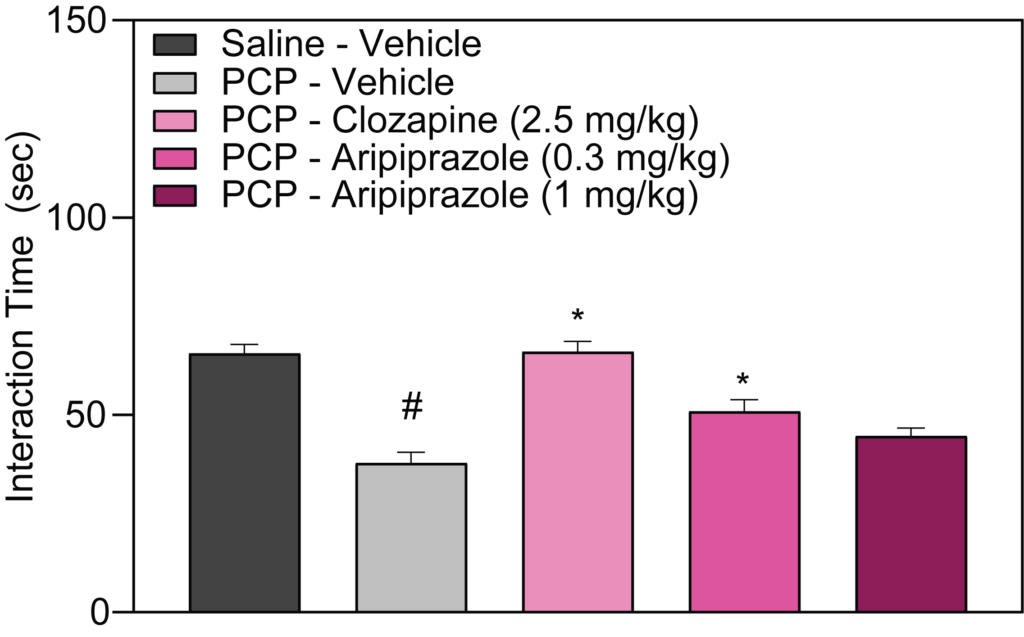
- PCP-induced deficits in Social Interaction
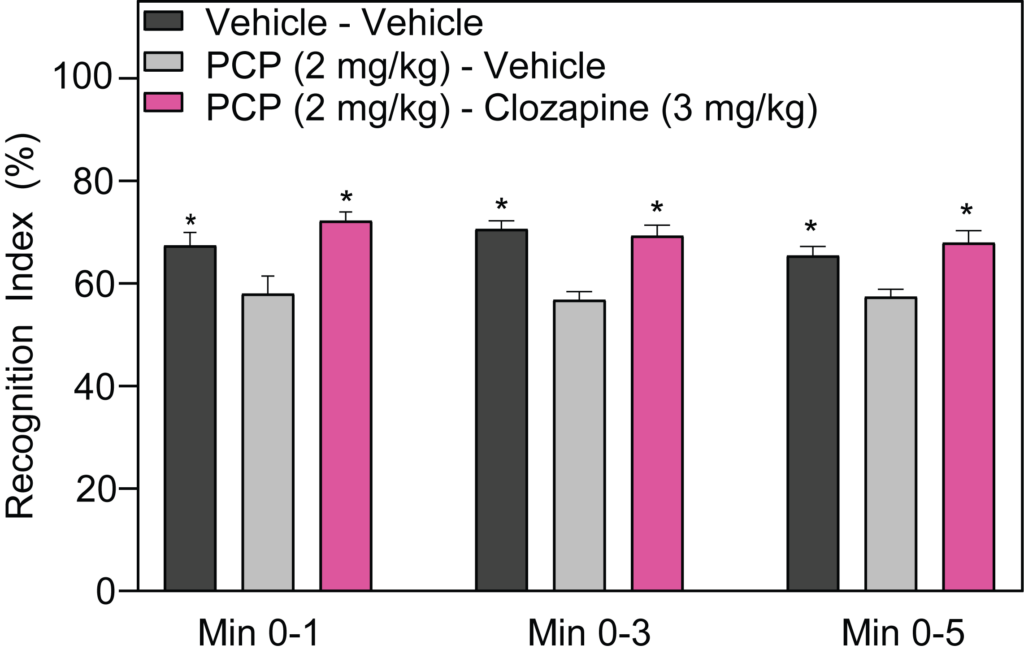
- PCP-induced deficits in Novel Object Recognition (NOR)
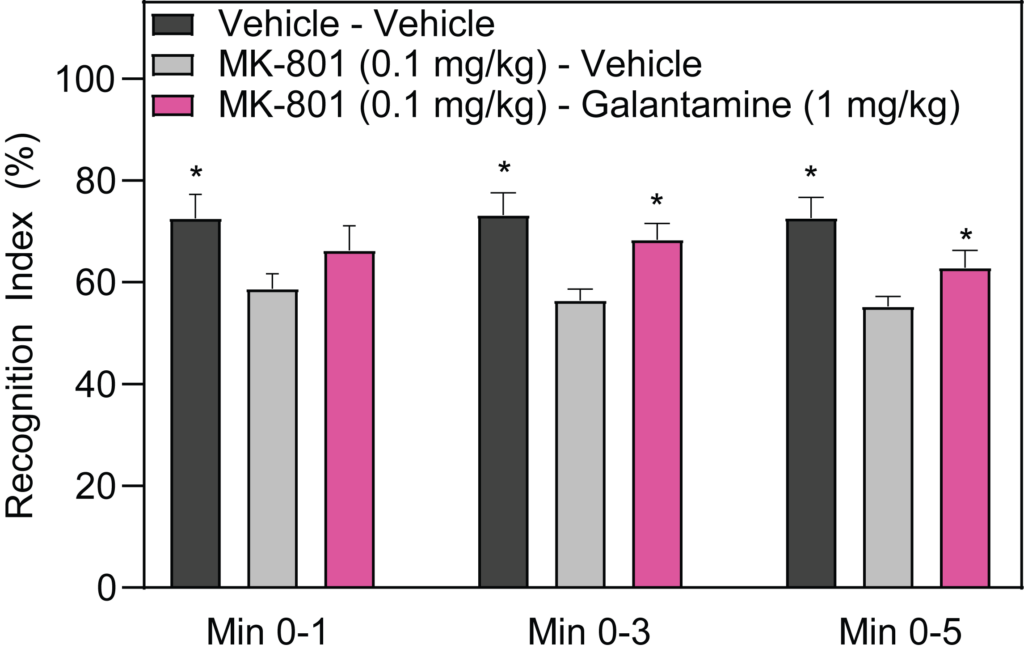
- PCP-induced deficits in Social Recognition
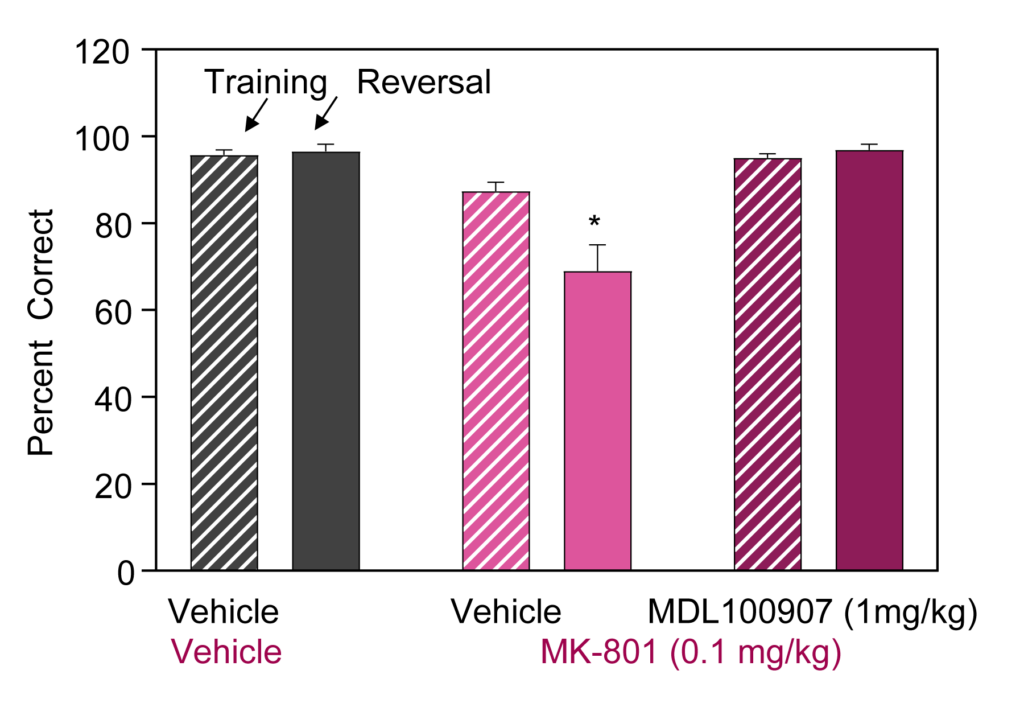
- MK-801-induced deficits in Reversal Learning
- Mismatch Negativity (MMN)
- Auditory Evoked Potentials (AEP)
Negative Symptoms: Cognitive and Social Deficits
Partner with PsychoGenics to accelerate your early-stage schizophrenia research and contribute to the discovery of transformative therapies for individuals living with this complex disorder.
Explore our areas of specialization: