Approximately 2% of individuals with ASD carry mutations in the Shank3 gene, which plays a crucial role in organizing neuronal connections. Shank3B-KO mice, developed by Professor Guoping Feng at MIT, harbor a deletion of exons 13-16 of the PDZ domains leading to deletion of the Shank3α and Shank3β isoforms and partial deletion of Shank3γ. Shank3B-KO mice exhibit social, sensory processing, and other behavioral abnormalities associated with ASD and thus, can be used as a model to evaluate novel therapies.
Social Challenges
Less Social Approach
Motor Challenges
Impairment on Rotarod
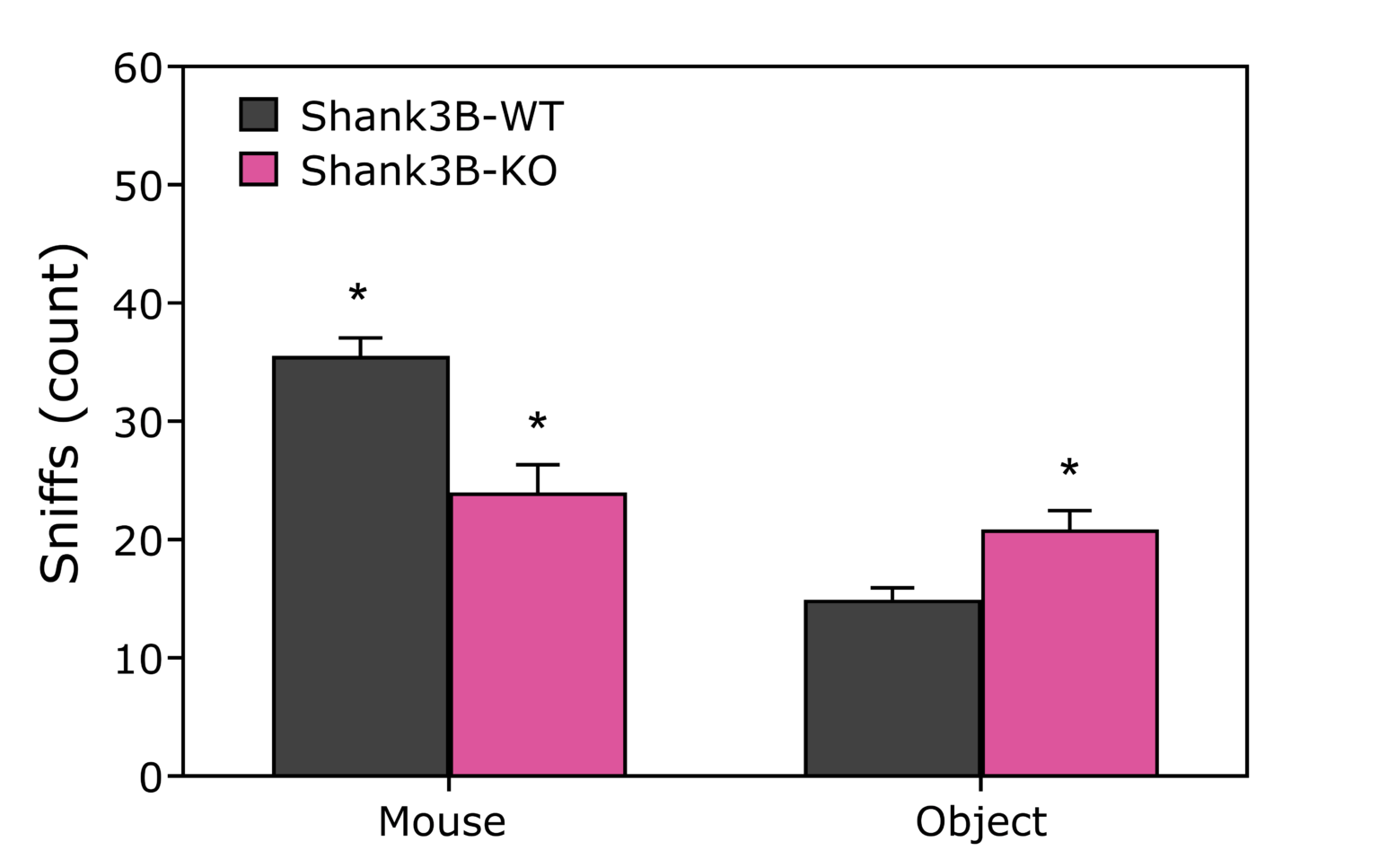
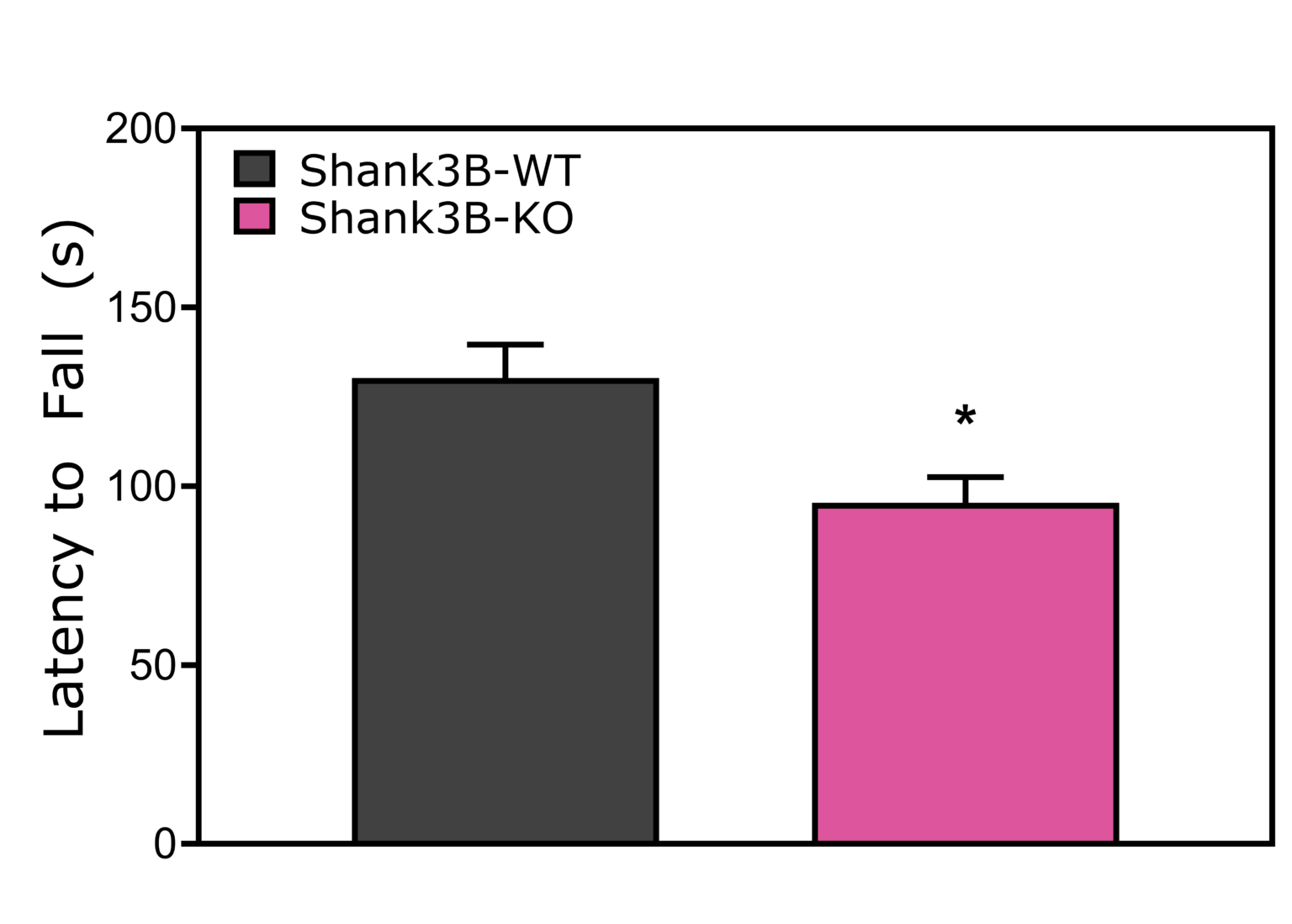
Male Shank3B-KO mice demonstrate reduced social interaction compared to WT mice in the 3-chamber social interaction test. They spend more time interacting with an inanimate object than a conspecific mouse.
Male Shank3B -KO mice show impaired rotarod performance. They fall quicker from a rotating rod compared to WT mice.
Sensory Motor Gaiting Deficits
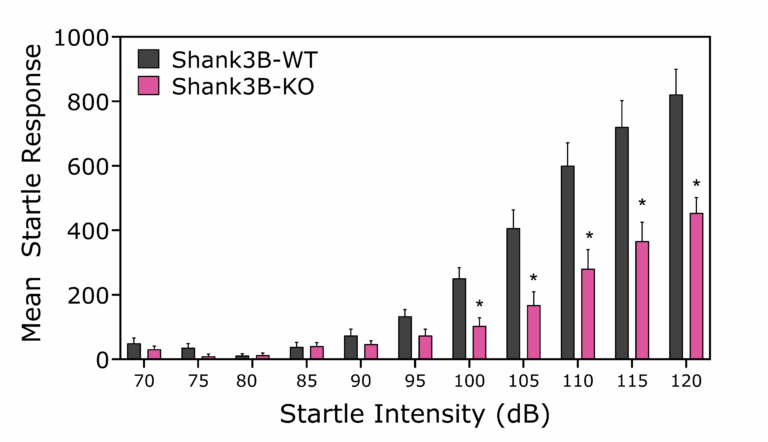
Male Shank3B-KO mice demonstrate reduced startle response compared to WT mice.
Reduced Synaptic Transmission in the Striatum
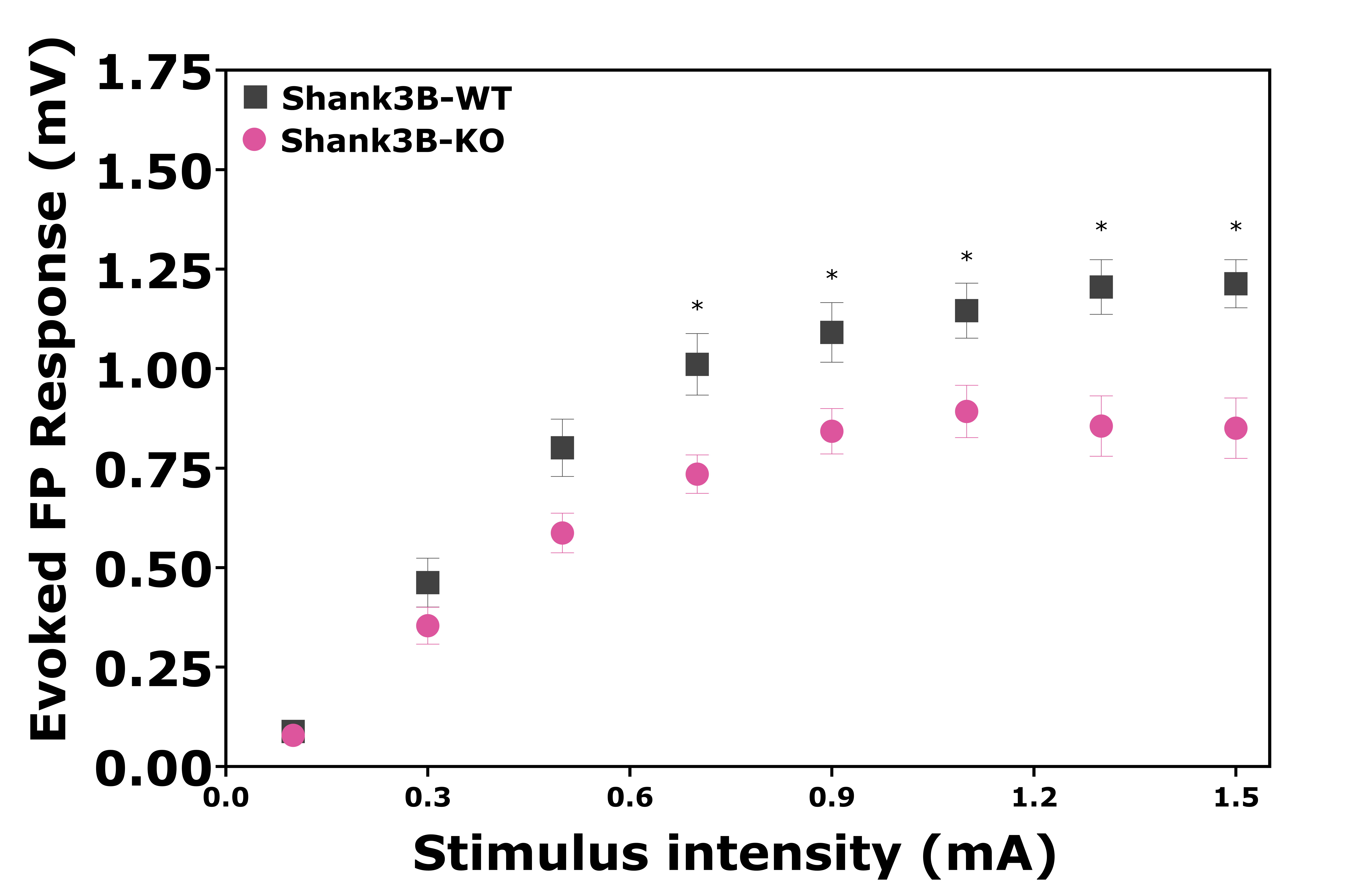
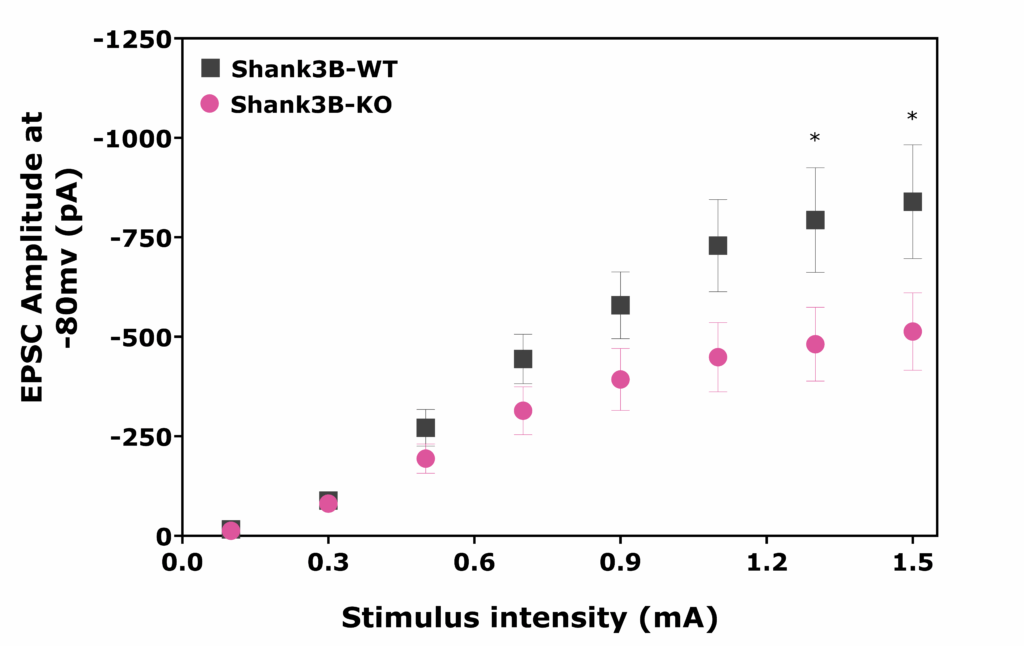
|
Synaptically driven extracellular field potentials in dorsolateral striatum that were evoked by stimulating corpus callosum are significantly smaller in male Shank3B- KO mice. |
Stimulus-evoked AMPA receptor-mediated whole-cell currents recorded in medium spiny striatal neurons are significantly reduced in male Shank3B-KO mice
Synaptic Markers
We examined synaptic markers, genes encoding for AMPA and NMDA receptor involved in cortico-striatal transmission, and genes encoding BDNF isoforms known for their role in plasticity.
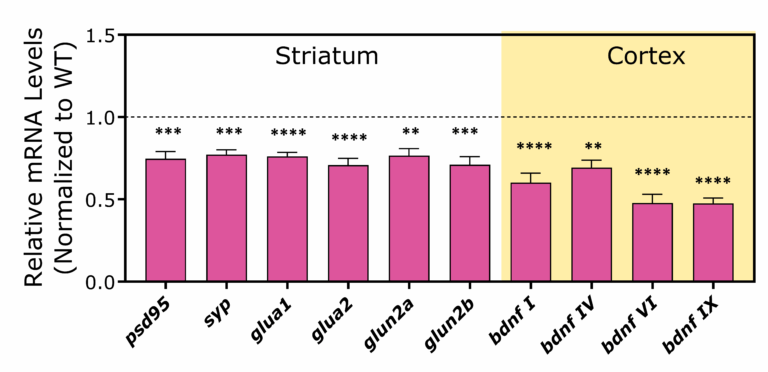
|
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of striatal and cortical tissues from 16-week old male Shank3B- KO and WT mice shows transcript level down-regulation in Shank3B-KO mouse brain tissues when compared to that of age-matched WT mice. Relative level of target genes (psd95, syp, glur1, glur2, nr2a, nr2b, bdnf isoforms I, IV, VI, IX) were first normalized to the housekeeping gene gapdh and then presented relative to tissue-matched WT cohorts. |